Introduction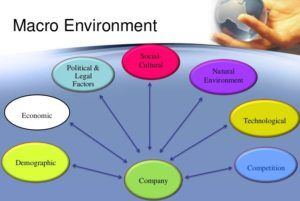
An organization’s success is influenced by factors operating in it’s internal and external environment; an organization can increase it’s success by adopting strategies which manipulate these factors to it’s advantage. A successful organization will not only understand existing factors but also forecast change, so that it can take advantage of change within the environments in which it operates.
Macro & Micro Environmental Factors
An organization’s operating environment has two parts; the Macro environment and the Micro environment.
Macro Environment – This contains external forces that an organization can’t directly control, instead organizations need to manage their macro environment in a way that benefits them.
Micro Environment – This is made up of internal factors which means that the organization is able to control their micro environment. To learn more about the micro environment (and marketing) click on this link Micro Environment.
PEST & PESTLE Analysis
A PEST analysis is used to identify the external forces affecting an organization/making up its Macro Environment. This is a simple analysis of an organization’s Political, Economical, Social and Technological environment. A PEST analysis incorporating legal and environmental factors is called a PESTLE analysis.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
The diagram below shows the 4 components of PEST Analysis
Political
The first element of a PEST analysis is a study of political factors. Political factors influence organizations in many ways. Political factors can create advantages and opportunities for organizations. Conversely they can place obligations and duties on organizations. Political factors include the following types of instrument:
- Legislation such as the minimum wage or anti discrimination laws.
- Voluntary codes and practices
- Market regulations
- Trade agreements, tariffs or restrictions
- Tax levies and tax breaks
- Type of government regime e.g. communist, democratic, dictatorship
Non conformance with legislative obligations can lead to sanctions such as fines, adverse publicity and imprisonment. Ineffective voluntary codes and practices will often lead to governments introducing legislation to regulate the activities covered by the codes and practices.
Economical
The second element of a PEST analysis in involves a study of economic factors. All businesses are affected by national and global economic factors. National (and global) interest rates and fiscal policy is set around economic conditions. The climate of the economy dictates how consumers, suppliers and other organizational stakeholders such as suppliers and creditors behave within society. An economy undergoing recession will have high unemployment, low spending power and low stakeholder confidence. Conversely a “booming” or growing economy will have low unemployment, high spending power and high stakeholder confidence.
A successful organization will respond to economic conditions and stakeholder behavior. Furthermore organizations will need to review the impact economic conditions are having on their competitors and respond accordingly. In the current business world, organizations are affected by economies throughout the world and not just the countries in which they are based or operate from. For example: a global credit crunch originating in the USA contributed towards the credit crunch in the UK in 2007/08.Cheaper labor in developing countries affects the competitiveness of products from developed countries. An increase in interest rates in the USA will affect the share price of UK stocks or adverse weather conditions in India may affect the price of tea bought in an English café.
A truly global player has to be aware of economic conditions across all borders and needs to ensure that it employs strategies that protect and promote its business through economic conditions throughout the world.
Social
The third aspect of PEST focuses its attention on forces within society such as family, friends, colleagues, neighbours and the media. Social forces affect our attitudes, interests and opinions. These forces shape who we are as people, the way we behave and ultimately what we purchase. For example within the UK people’s attitudes are changing towards their diet and health. As a result the UK is seeing an increase in the number of people joining fitness clubs and a massive growth for the demand of organic food. Products such as Fitbit attempt to deal with society’s concern, about lack of exercise.
Population changes also have a direct impact on organizations. Changes in the structure of a population will affect the supply and demand of goods and services within an economy. Falling birth rates will result in decreased demand and greater competition as the number of consumers fall. Conversely an increase in the global population and world food shortage predictions are currently leading to calls for greater investment in food production. Due to food shortages African countries such as Uganda are reconsidered their rejection of genetically modified foods.
In summary organizations must be able to offer products and services that aim to complement and benefit people’s lifestyle and behavior. If organizations do not respond to changes in society they will lose market share and demand for their products and services.
Technological
Unsurprisingly the fourth element of PEST is technology, as you are probably aware technological advances have greatly changed the manner in which businesses operate. Organizations use technology in many ways, they have
- Technology infrastructure such as the internet and other information exchange systems including the telephone and conference calling.
- Technology systems incorporating a multitude of software which help them manage their business
- Technology hardware such as mobile phones, computers, photocopiers and fax machines which transmit and record information.
Technology has created a society which expects instant results. This technological revolution has increased the rate at which information is exchanged between stakeholders. A faster exchange of information can benefit businesses as they are able to react quickly to changes within their operating environment. However an ability to react quickly also creates extra pressure as businesses are expected to deliver on their promises within ever decreasing time scales. For example the Internet is having a profound impact on the marketing mix strategy of organizations. Consumers can shop 24 hours a day from where ever they want and however they want via smart phones, laptops and tablets.
The pace of technological change is so fast that the average life of a computer chip is approximately 6 months. Technology is utilized by all age groups, children are exposed to technology from birth and a new generation of technology savvy pensioners known as “silver surfers” have emerged. Technology will continue to evolve and impact consumer habits and expectations, organizations that ignore this will hinder their success.
PESTLE
A PEST analysis is sometimes expanded to incorporate legal and environmental factors; this is known as a pestle analysis. There are many statutes books containing company law as almost every aspect of an organization’s operation is controlled through legislation from treatment of employees through to health and safety. Legal factors are important as organizations have to work within legislative frameworks. Legislation can hinder business by placing onerous obligations on organizations. On the other hand legislation can create market conditions that benefit business.
Also Study:
Macro Environment Factors for Ongoing Global Markets